
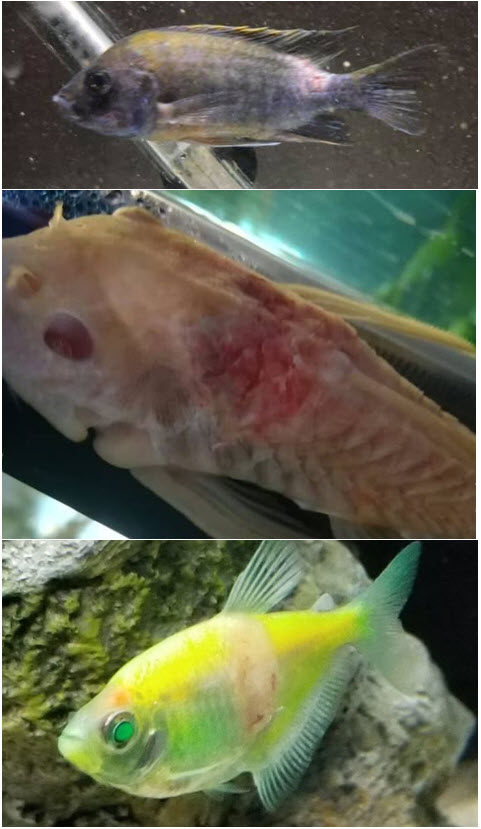
Saddleback and white spot can become pink or red open lesions or ulcers. Ulcers caused by bacteria come on quickly and are typically flat. This contrasts to the ulcers caused by fish TB which come on slowly and are raised bumps that slowly break open into raised edged ulcers. Ulcers in fish are most often gram-negative bacteria (columnaris, aeromonas, etc.).
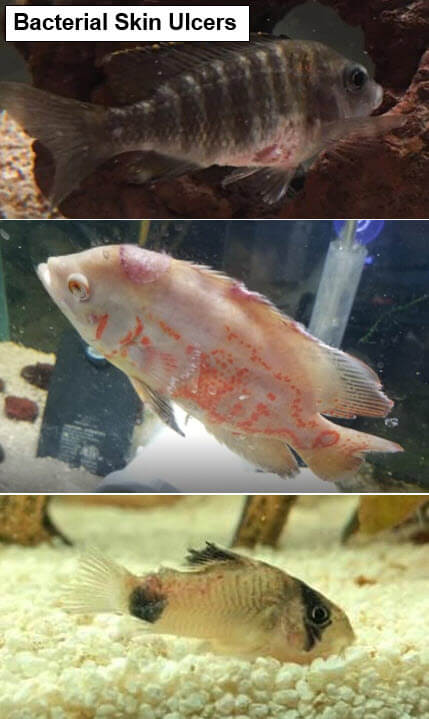

Note that bacteria are often secondary invaders and ulcers are often secondary infections. Often time the primary disease is something like anchor worms or flukes. The anchor worms and the flukes break the skin of the fish and allow bacteria to enter, creating the ulcer. Bites and ramming by other fish can also break the skin and allow bacteria to enter and start an ulcer.

Treatment
Ulcers should be treated with broad spectrum antibiotics (Midland Vet Service Aqua-Mox, VetDepot Amoxicillin, Fishbiotic Ampicillin, Mardel Maracyn 2, SeaChem KanaPlex, API Fin And Body Cure) added to the food. These antibiotics are generally only available over the internet.
Bacterial infections are most effectively treated with antibiotics in the food. Many believe (and the instructions on the antibiotics say!) that antibiotics need to be added to the water. They are simply incorrect. This controversial topic is covered in the following link:
It is easy to make medicated food. Heat 1/4 cup water (two ounces or 58 milliliters, not a lot) in the microwave. Then blend one 1/4 ounce of plain gelatin (Knox gelatin, one envelope), pectin or agar into the hot water with vigorous stirring. Take two tablespoons of dry commercial fish food (pellets or flake) and mix it with just a little of the hot water/ gelatin mixture. Add hot water/gelatin until you get a paste like consistency. If it gets too watery just add more food.
Then add just a “smidgen” (roughly 1/16 teaspoon, a 1% to 2% addition) of medication to the mud. If you are using more than one medication mix the medications together, then use just a “smidgen” of the mixture. If you are using a packet of medication, take just a “smidgen” of the packet contents. Mix and mash the whole mass thoroughly. Spread it out into a pancake about 1/8th inch (3 mm) thick on a plastic film or a plate. Then put in the refrigerator. If you plan on keeping it for more than two weeks put it in a small plastic bag and freeze.
All the fish in the aquarium should be fed a steady diet of the antibiotic laced food for at least ten days. Note that the exact amount of medication which goes into the food is not very important. Antibiotics can be overdosed pretty much with abandon as they are only toxic in large doses over a period of months. Note this gel food is 80% water. So it will require ten eyeballs per day of food per fish (six fish = 60 fish eyeballs = six times ten).
Treatment needs to be for at least two weeks. If it is one or two fish transfer the fish to a hospital aquarium and treat. If more than two fish have the problem one must treat the whole aquarium. Note antibiotics in the food do not affect the filters so they can be left in place and operating.
If you can’t resist the urge to treat the water, remove the biofiltration media (including sponge and/or foam) in the filters and put it in an open container for the duration of the treatment. Sometimes antibiotics kill the beneficial bacteria and sometimes they don’t. In any case the filter media will denature the antibiotics. Monitor the ammonia and would do a 50% water change if it spikes above 1 ppm. Reduce the amount of food fed by 2/3 rds.
Note that if antibiotics are not available, it is quite easy to take a pill or capsule of human antibiotic and use it for fish. If it is a pill just grind it up. Just be aware that the human antibiotics are about ten times more potent than the aquarium antibiotics, so just a “smidgen” in the food is more than enough. This is a very good option for the folks in Europe or Canada, where fish antibiotics are illegal.
If one has more than one fish with a bacterial disease, one must treat the whole aquarium. This is an emergency. Don’t fool around with herbs, tree leaf oils or some ineffective treatment. Ben Ochart treated a bacterial infection with Pimafix and Melafix. They did nothing to stop the infection. He lost a lot of large beautiful fish before he stopped the infection with antibiotics. This link covers the snake oil medications such as Melafix and Pimafix:
The entire topic of bacterial infections in tropical aquarium fish is covered in more detail in this link:
.
Aquarium Science Website
The chapters shown below or on the right side in maroon lead to close to 400 articles on all aspects of keeping a freshwater aquarium. These articles have NO links to profit making sites and are thus unbiased in their recommendations, unlike all the for-profit sites you will find with Google. Bookmark and browse!
.

